ESG & GRI Reporting

What is ESG
ESG addresses many topics and stakeholders. ESG represents the company’s efforts to systematically assess, manage, and monitor risks of material potential impact to the strategic and financial decisions of the company.
The term ESG is often used as a synonym for sustainability, CSR, public relations, social investment, or environmental compliance. While some of these elements may factor into an ESG program, at the center of ESG is the management of risk and the preservation of shareholder value.
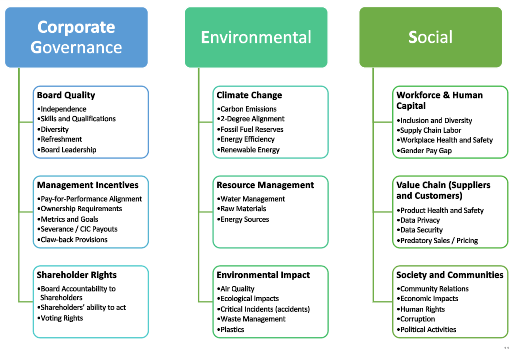
Key Components of ESG
- Corporate governance issues apply universally across all industries.
- Good governance of corporate, environmental, and social issues creates sustainable companies
- Material environmental and social issues vary significantly by industry and may even be company-specific, depending on the level of materiality of each factor.
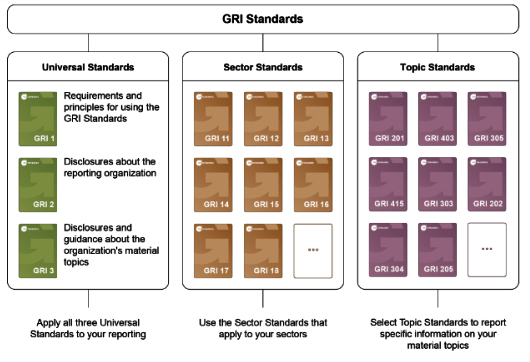
Introduction to GRI
- GRI provides a standardized framework for sustainability reporting.
- It covers economic, environmental, and social aspects, promoting transparency and accountability.
- Stakeholder engagement and materiality assessments are key components.
- Reporting helps organizations track progress, set targets, and drive continuous improvement.
- GRI has 3 types of standards:
- Universal Standards
- Sector Specific Standards
- Material Topic Standards
Benefits of GRI

Who can Publish GRI Standard Report?
Frequently Asked Questions
ESG reporting helps organizations enhance their reputation, attract investment, mitigate risks, and drive long-term value creation. It also fosters transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement in sustainability performance.
We employ robust data management processes, validation procedures, and quality assurance measures to ensure the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of ESG performance data reported by organizations.
Common ESG metrics include greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, water usage, waste generation, employee diversity and inclusion, health and safety performance, ethical business practices, and community engagement.
Organizations can use ESG reporting to engage stakeholders by providing transparent, timely, and relevant information on their sustainability performance, goals, and initiatives. This can help build trust, foster dialogue, and demonstrate commitment to responsible business practices.
While ESG reporting is not mandatory for all organizations, there is increasing pressure from investors, regulators, and other stakeholders for companies to disclose ESG-related information voluntarily. Many stock exchanges, regulatory bodies, and industry associations have also introduced ESG reporting requirements or guidelines.
Our Projects
Our portfolio showcases the diverse range of projects we have delivered within the continuity of our business relationships in the MEP, architectural, retail and residential sectors.